English Tenses Explained with Examples – The Complete Guide
Learning English tenses can feel overwhelming. With 12 main tenses and many variations, learners often ask: How do I use them correctly? This is why thousands of students search for “English tenses explained with examples.”
The confusion usually comes from not knowing when to use past, present, or future forms. Many learners mix up continuous and perfect tenses, or use the wrong tense when writing essays, speaking, or sending emails.
This article will give you a quick answer, explain the origin of English tense rules, compare usage in British and American English, and highlight common mistakes. You will also see real-life examples, Google Trends data, and FAQs. By the end, you’ll have a clear, simple, and professional guide to mastering English tenses.
English Tenses Explained with Examples – Quick Answer
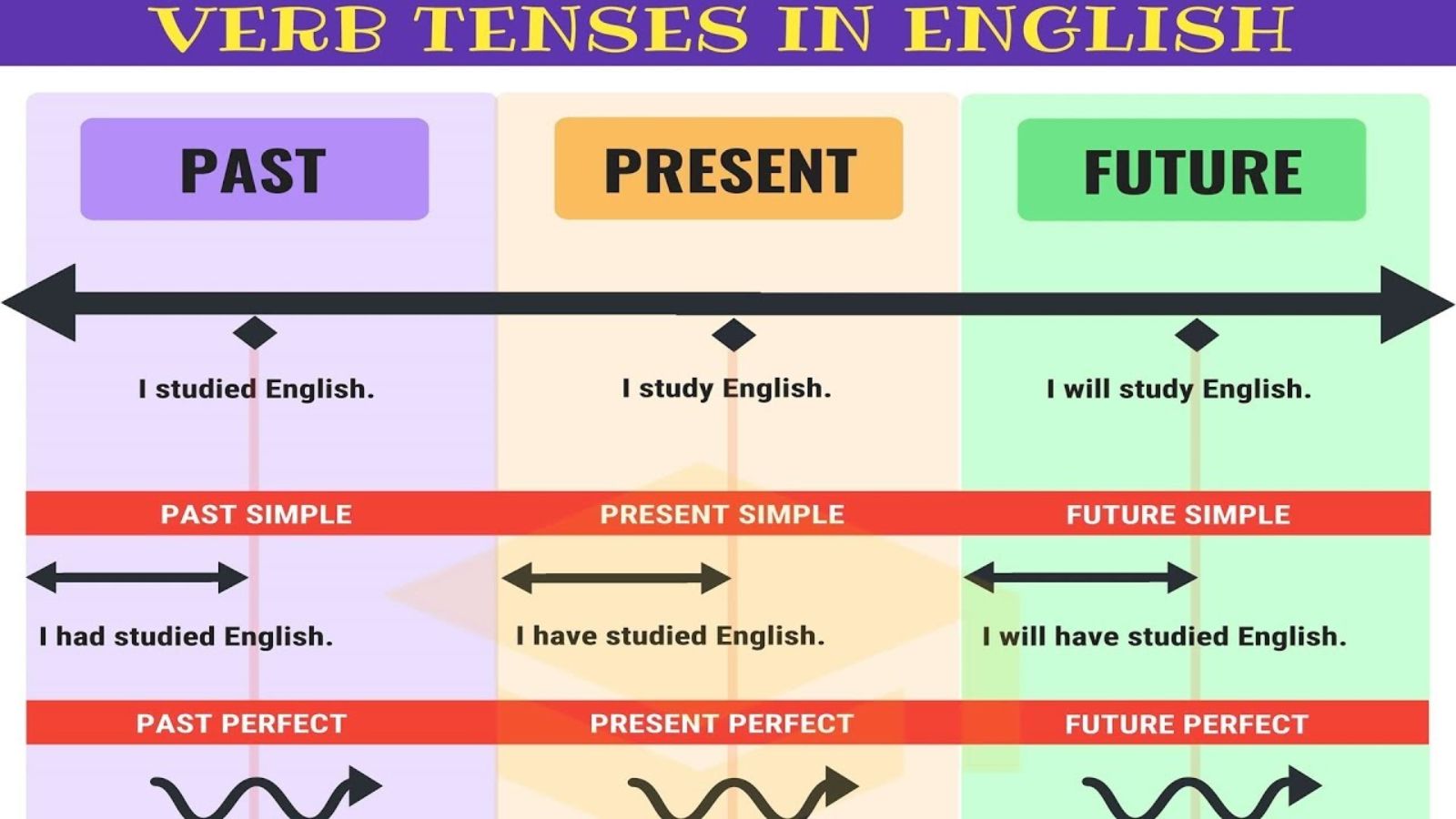
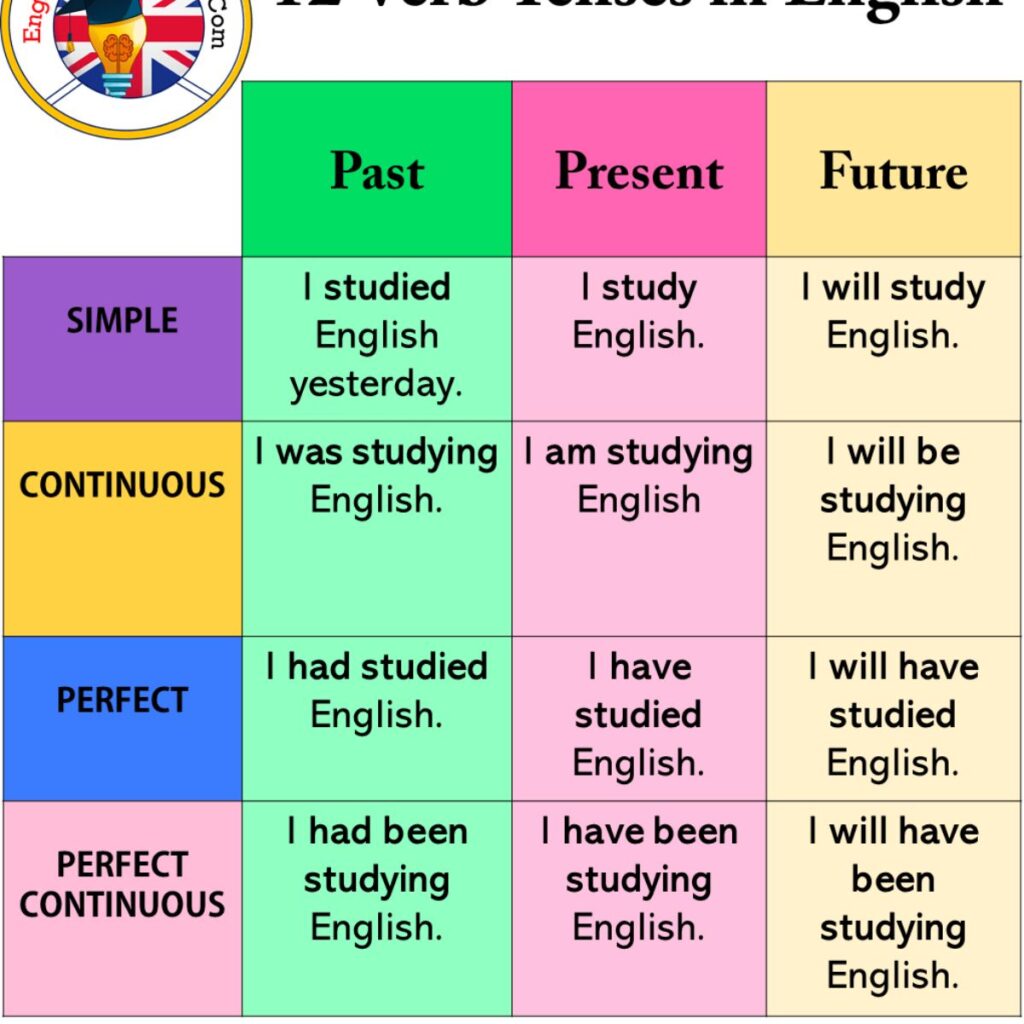
English has 12 main tenses, grouped into past, present, and future.
👉 Examples:
- Present Simple: I write every day.
- Present Continuous: I am writing now.
- Past Simple: I wrote yesterday.
- Future Simple: I will write tomorrow.
Each tense shows when an action happens and whether it is finished, continuing, or planned.
The Origin of English Tenses Explained with Examples
The word “tense” comes from the Latin word tempus, meaning “time.” In Old English, verbs had fewer tense forms, mostly present and past. Over centuries, English grammar expanded with helping verbs (do, have, will, be) to express more complex times and actions.
That’s why we now have 12 tenses instead of only two. Modern grammar books use examples to make tenses easier to understand for learners worldwide.
British English vs American English Tenses
British and American English both use the same tenses, but with some differences:
| Tense/Use | British English Example | American English Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Present Perfect | I have just eaten. | I just ate. | Americans often use Past Simple instead of Present Perfect. |
| Future Plans | I shall go tomorrow. | I will go tomorrow. | “Shall” is rare in US English. |
| Past Simple | I learnt a lot. | I learned a lot. | Spelling difference in some verbs. |
So, while the tenses are the same, usage varies slightly.
Which Version Should You Use?
- If writing for US readers: Prefer American style (e.g., I just ate).
- If writing for UK/Commonwealth readers: Use British style (I have just eaten).
- For global audiences: Stick to clear, neutral forms. Avoid rare words like shall.
👉 Rule of thumb: Know your audience before choosing tense style.
Common Mistakes with English Tenses Explained with Examples
- Using Present Simple instead of Present Continuous → I write now ❌ → I am writing now ✅
- Mixing up Present Perfect and Past Simple → I have seen him yesterday ❌ → I saw him yesterday ✅
- Using “will” for fixed timetables → The bus will leave at 8 ❌ → The bus leaves at 8 ✅
- Forgetting third-person “-s” → She go to school ❌ → She goes to school ✅
English Tenses Explained with Examples in Everyday Use
- Emails: I have attached the file. (Present Perfect)
- News Reports: The President is meeting leaders today. (Present Continuous)
- Social Media: I was watching the game last night! (Past Continuous)
- Formal Writing: Research has shown clear results. (Present Perfect)
Tenses shape how professional or casual your message sounds.
English Tenses Explained with Examples – Google Trends & Usage Data
Search interest for “English tenses explained with examples” is highest in:
- India, Pakistan, Nigeria: Learners preparing for exams.
- Middle East: Students learning English for jobs.
- US & UK: Teachers looking for easy ways to explain grammar.
| Country | Top Search Phrase | Popular Audience |
|---|---|---|
| India | English tenses explained with examples | Students, UPSC/IELTS learners |
| Pakistan | Tenses with examples | Matric/Intermediate students |
| Nigeria | Learn English tenses | Job seekers |
| USA | English grammar tenses | Teachers & writers |
FAQs
1. How many English tenses are there?
There are 12 main tenses, grouped into past, present, and future.
2. What is the easiest way to learn tenses?
Use simple examples and practice with everyday sentences.
3. What is the difference between past simple and present perfect?
Past Simple shows a finished time (I ate yesterday), while Present Perfect links past to now (I have eaten already).
4. Do British and American English use different tenses?
They use the same tenses, but Americans prefer Past Simple where Brits use Present Perfect.
5. Can I avoid using complex tenses?
Yes, but advanced writing often needs Perfect and Continuous forms.
6. Do tenses matter in spoken English?
Yes. Using the wrong tense can confuse listeners.
7. How can I practice?
Write 5–10 sentences daily using different tenses, then check with examples.
Conclusion
Understanding English tenses is key to speaking and writing clearly. The question “English tenses explained with examples” comes from learners who need simple explanations.
We learned that English has 12 main tenses, all used to show time and action. British and American English share the same system but differ in some expressions. Common mistakes include mixing tenses, forgetting rules, or using the wrong form for time expressions.
The best way forward is to practice with examples, know your audience (US vs UK), and focus on clarity. With these rules, you can master tenses for exams, professional writing, and daily communication.